November 2024 Methodology Updates (2/n)

This article is an automatically translated version of the original Japanese article. Please refer to the Japanese version for the most accurate information.
This is a newsletter from Sustainacraft Inc.
Methodology Updates is a series that covers methodologies for Carbon and Biodiversity Credits. This article introduces minor updates to Gold Standard and VCS methodologies announced from last month to this month.
Release of a New Cover Crops Module (Gold Standard)
VCS Methodology Updates (Verra)
Module update for REDD+ Methodology VM0048 and CCP certification
Update to IFM Methodology VM0010 (Conservation Forestry)
For inquiries, please contact us here.
Release of a New Cover Crops Module (Gold Standard)
<Source>
- [1] https://www.goldstandard.org/news/new-cover-crops-soil-organic-carbon-activity-module-released
In early October, Gold Standard newly added Cover Crops as a module to its Soil Organic Carbon Framework Methodology (SOCFM) ([1]). As introduced in the previous newsletter, SOCFM is a methodology that covers multiple activities aimed at increasing Soil Organic Carbon, and it corresponds to Verra's ALM Methodology, VM0042.
Unlike VM0042, SOCFM only covers activities for which a corresponding module exists. With the addition of this module, there are now six activity types covered.
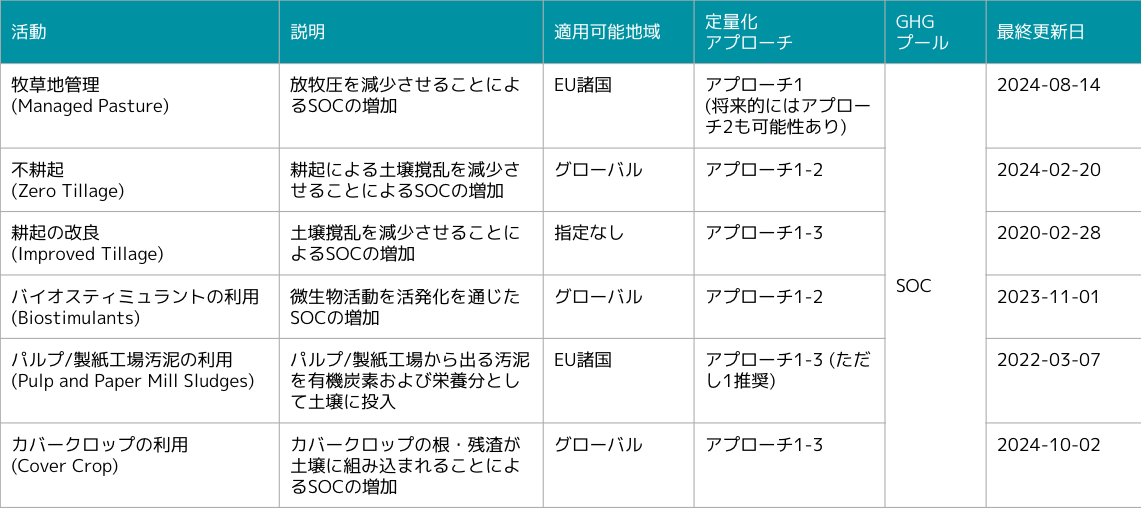
Cover crops are plants primarily grown during the fallow period of main crops for the purpose of soil protection and improvement. Typical cover crops include graminaceous crops (e.g., rye), leguminous crops (e.g., Chinese milk vetch, hairy vetch), and brassicaceous crops. The main benefits of cover crops generally include the following:
- Supply of Organic Matter: Supplies organic matter to the soil through the natural decomposition of crop roots and stems.
- Prevention of Soil Erosion: Covers the ground surface, preventing soil runoff and erosion caused by rain and wind.
- Improvement of Soil Fertility: Legumes, in particular, fix nitrogen, increasing nitrogen levels in the soil.
- Weed Suppression: By growing densely and covering the surface, they suppress weed growth and reduce herbicide use.
- Moisture Retention: By covering the surface, they suppress evaporation and retain soil moisture.
- Pest and Disease Suppression: Some cover crops inhibit the occurrence of specific pests and pathogens.
Before entering the next cropping cycle, processes are carried out to terminate cover crops1. Specifically, these methods include plowing them into the soil, killing them with herbicides, or allowing livestock to graze on them.
The module added this time is a tool specifically for quantifying SOC increase through the supply of organic matter, as mentioned in the first point above. Below, we will introduce some characteristic points of this module.

